Climate Change and Food Security
Drought
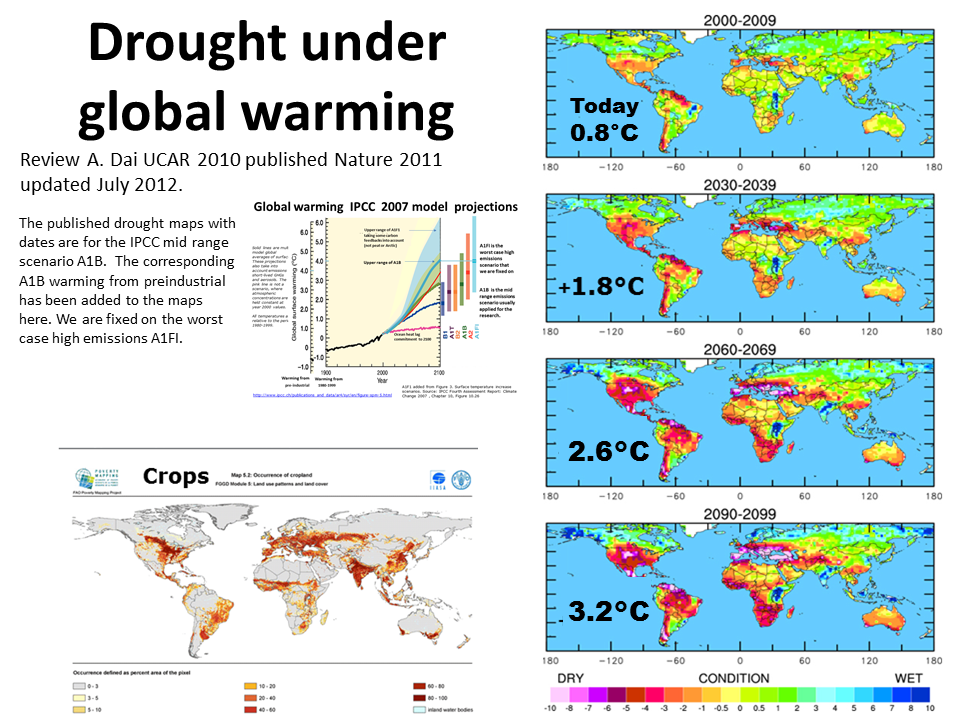
Drought
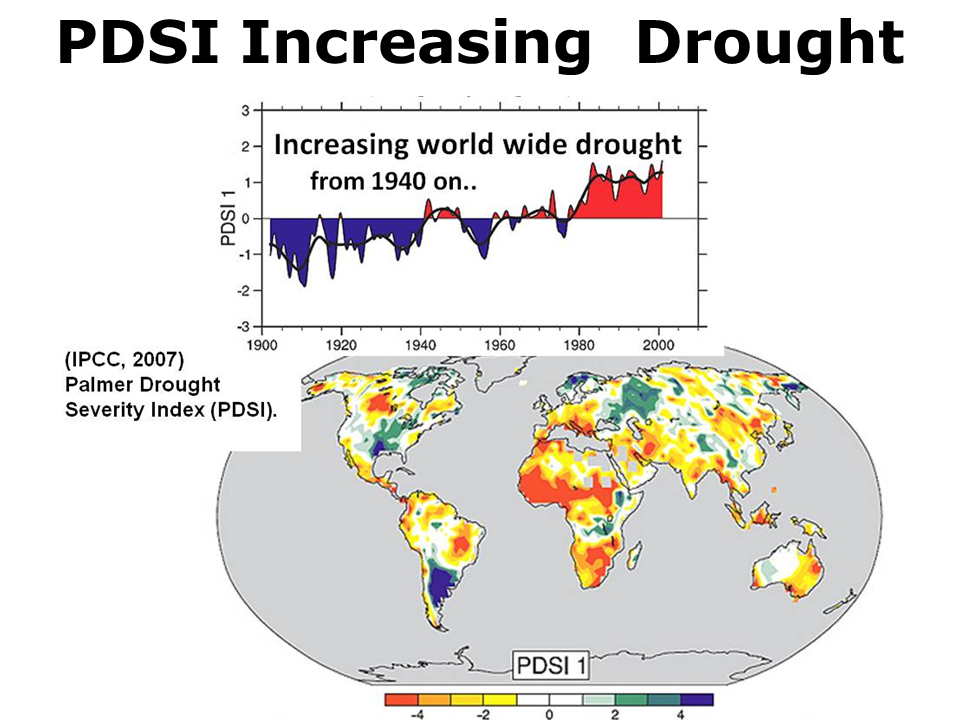
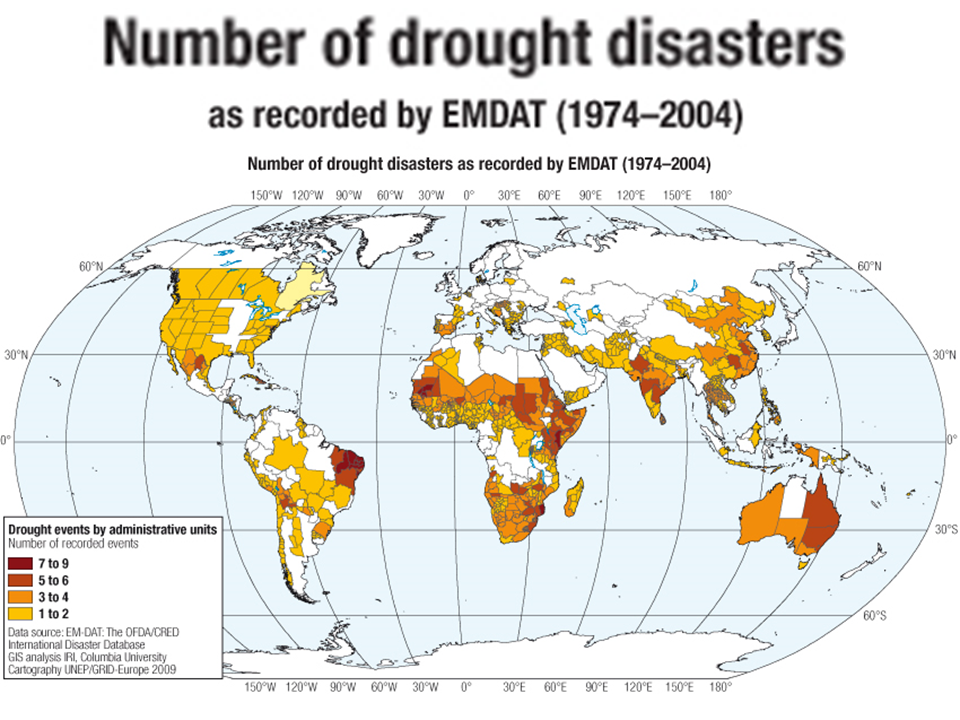
The dryness and drought trend standard measure is the the Palmer Drought Severity Index. The 'Increasing Drought' map shows the global PDSI from 1900 to 2002. For most areas, drier (red and yellow) conditions have progressively increased over the century with a huge jump from 1880 to 1985. The bottom figure shows the trend over time of increasing drought, indicating that for much of the world, droughts are more common.(IPCC 2007).
The PDSI is being questioned to assess drought under climate change because it may overestimate area increase.
The PDSI is being questioned to assess drought under climate change because it may overestimate area increase.
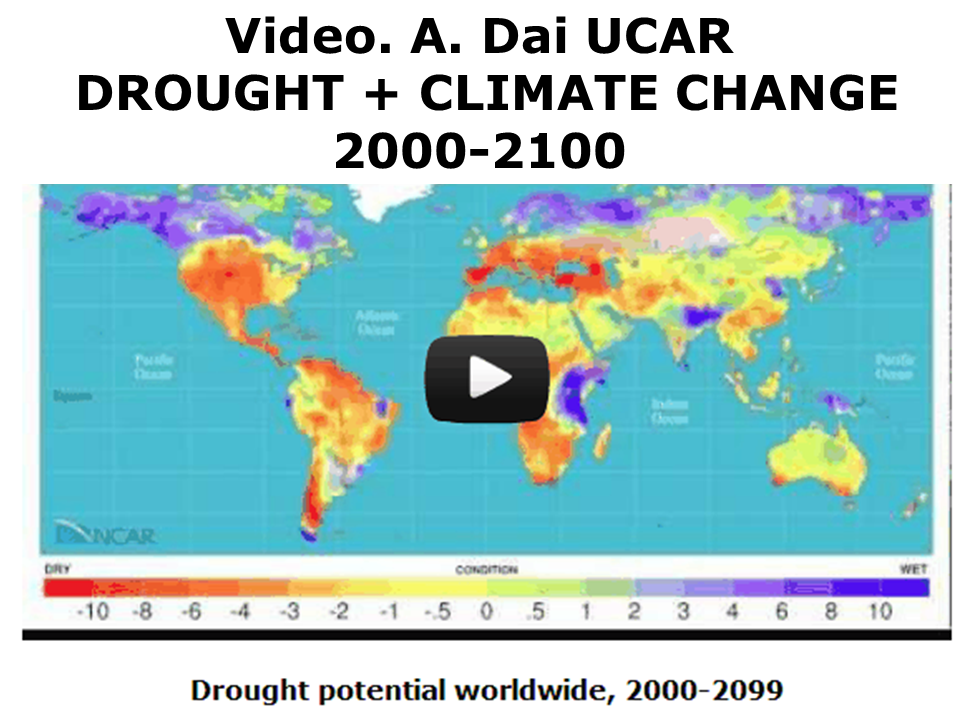
Climate Change: Drought may threaten much of globe within decades
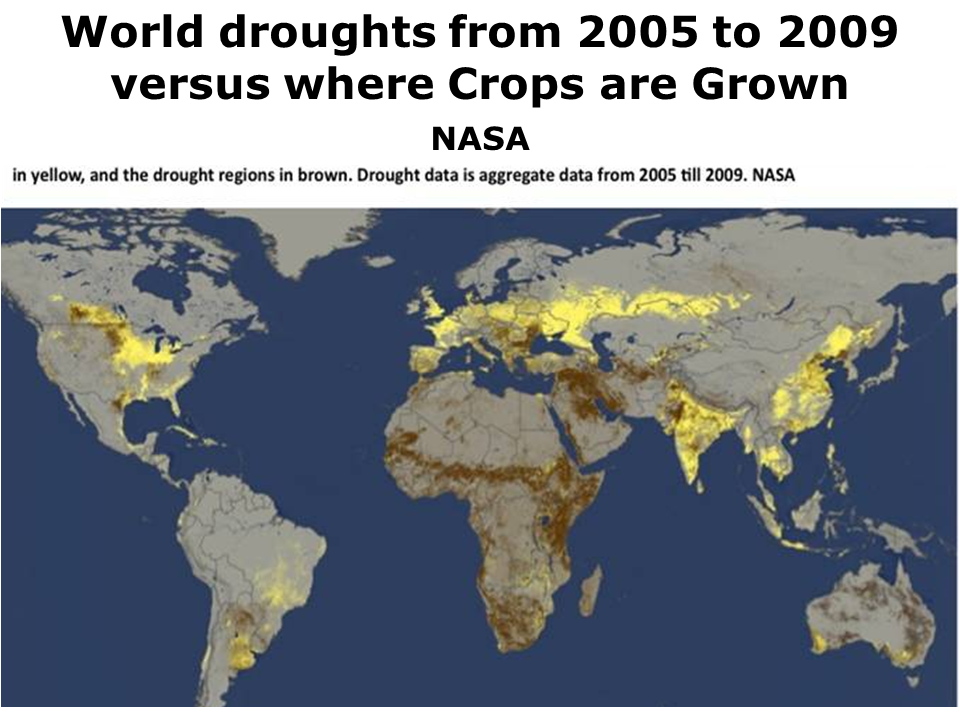
UCAR site of research by A Dai The drought projections affect all the world's best food producing regions. At 1.8C severe drought affects all the world's food producing regions.
For more in depth see Dai 2011 Drought Under Global Warming Review
UCAR site of research by A Dai The drought projections affect all the world's best food producing regions. At 1.8C severe drought affects all the world's food producing regions.
For more in depth see Dai 2011 Drought Under Global Warming Review
Increasing drought affecting the world's best food producing regions in the Northern hemisphere threatens world grain reserves and world food security (Center for Climate and Security).
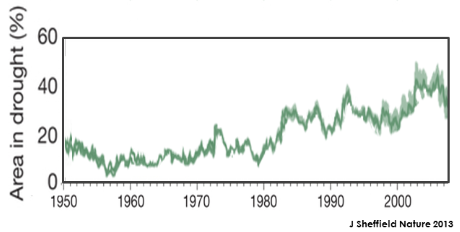
Nov 2013 K Trenberth A Dai Global warming and changes in drought shows a global drying trend 1980-2010, future drought will set in faster and be more intense.
A Dai (UCAR) is the top world expert in drought modeling past and projected global drought. Remember we are already locked into a warming today's 2-3X today's 0.8C because of the climate change commitment.
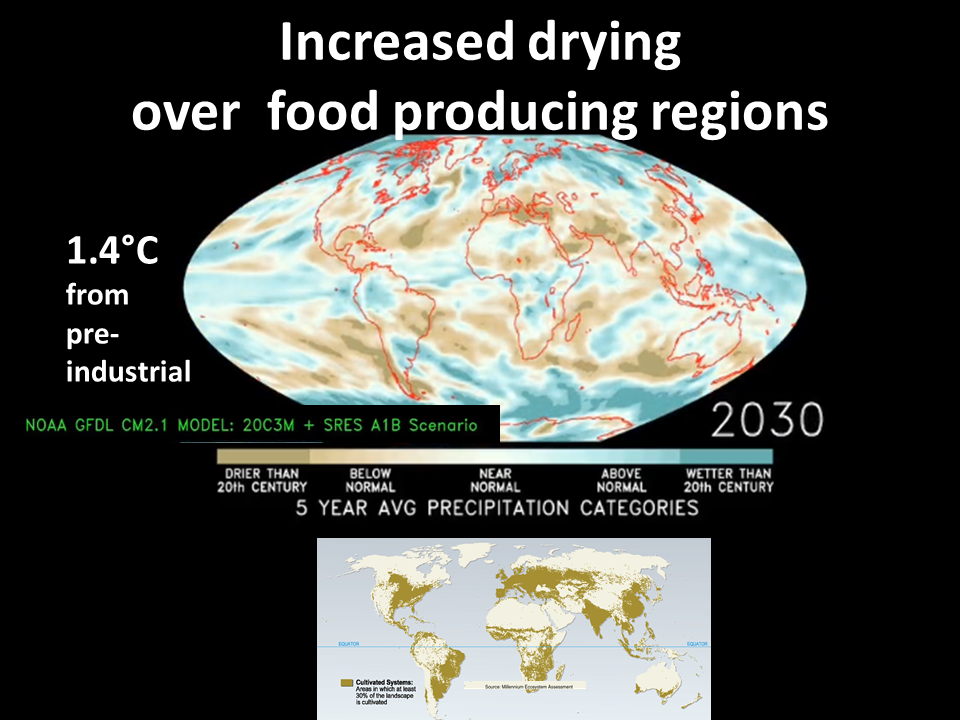
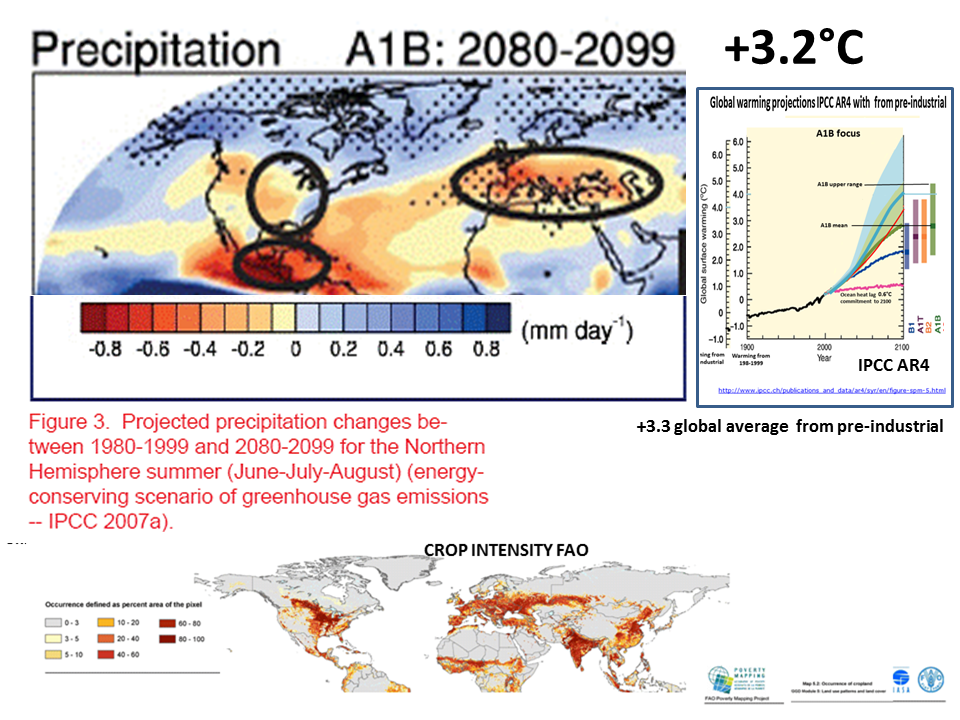
Global warming induced drying is projected by models to affect major food producing regions as increased precipitation moves towards the poles . While drought occurs in Summer, Winter rainfall is important because it replenishes water sources.
Since 2000 extreme heat and drought has affected US and other Northern hemisphere food producing regions, affecting Western Europe. Extreme NH drought has affected Western Europe, Russia, USA, China and India.
Drought Is Increasing - more than doubled world wide according to A. Dai 2010.
However since 2012 the science on how much global drought has increased has been questioned.
Tne IPCC AR5 says drought has increased in certain regions -Mediterranean and West Africa
and likely decreased in central North America and north-west Australia since 1950 (IPCC AR5 WG1 Ch2. Extreme Events).
The most recent paper is by A Dai 2012 and revised who upon review finds observations and models show world drought is increasing under global warming.
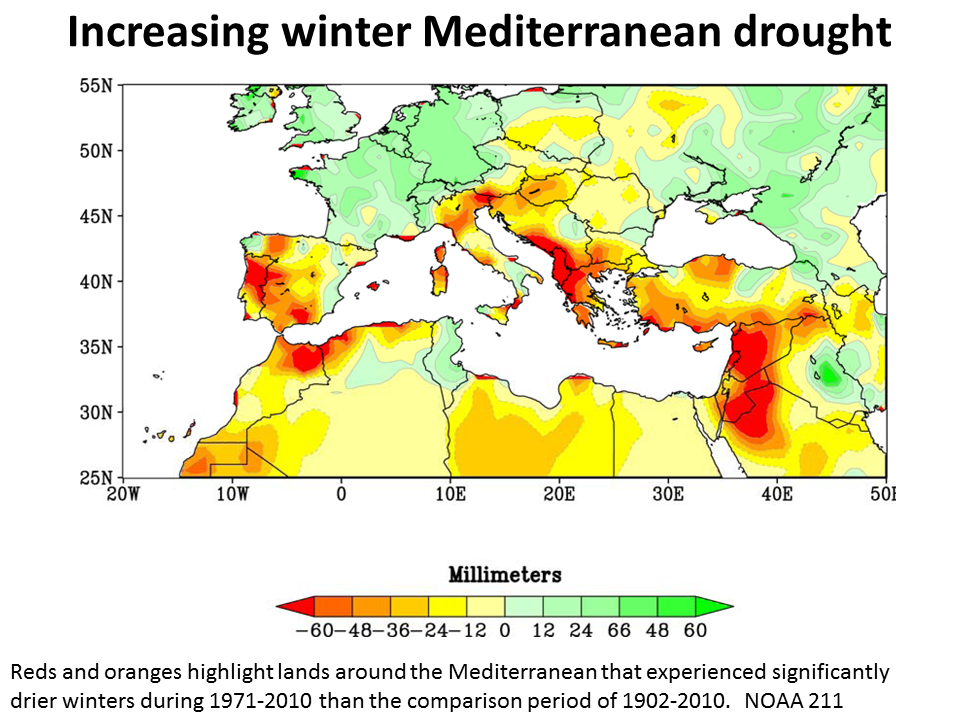
While we think of drought being a summertime event winter drought also matters. In 2011 NOAA reported that dangerous wintertime drought was increasing around the Mediterranean.
Drought, which is water shortage, can be defined in a number of ways. It will continue to increase as global warming continues and global temperatures increase.
Global warming related increased drought affected the temperate NH late 1990s and early 2020s.
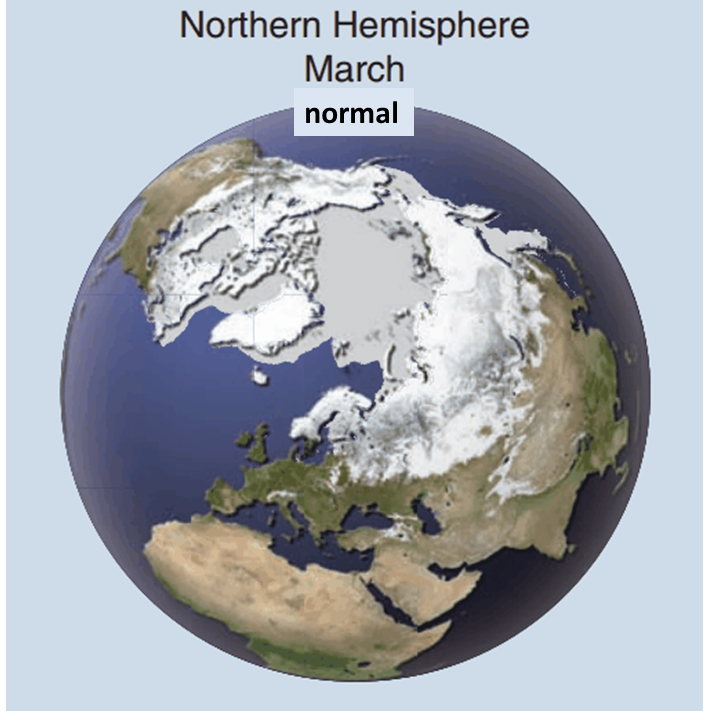
Over the past few years it looks like Northern hemisphere drought is increasing, affecting all the world's best food producing regions. The rapid loss of Arctic cooling snow and ice albedo cooling is projected to increase N. hemisphere drought, so may now be a factor.
Nov 2013 K Trenberth A Dai Global warming and changes in drought shows a global drying trend 1980-2010, future drought will set in faster and be more intense.
A Dai (UCAR) is the top world expert in drought modeling past and projected global drought. Remember we are already locked into a warming today's 2-3X today's 0.8C because of the climate change commitment.
Global warming induced drying is projected by models to affect major food producing regions as increased precipitation moves towards the poles . While drought occurs in Summer, Winter rainfall is important because it replenishes water sources.
Since 2000 extreme heat and drought has affected US and other Northern hemisphere food producing regions, affecting Western Europe. Extreme NH drought has affected Western Europe, Russia, USA, China and India.
Drought Is Increasing - more than doubled world wide according to A. Dai 2010.
However since 2012 the science on how much global drought has increased has been questioned.
Tne IPCC AR5 says drought has increased in certain regions -Mediterranean and West Africa
and likely decreased in central North America and north-west Australia since 1950 (IPCC AR5 WG1 Ch2. Extreme Events).
The most recent paper is by A Dai 2012 and revised who upon review finds observations and models show world drought is increasing under global warming.
While we think of drought being a summertime event winter drought also matters. In 2011 NOAA reported that dangerous wintertime drought was increasing around the Mediterranean.
Drought, which is water shortage, can be defined in a number of ways. It will continue to increase as global warming continues and global temperatures increase.
Global warming related increased drought affected the temperate NH late 1990s and early 2020s.
Over the past few years it looks like Northern hemisphere drought is increasing, affecting all the world's best food producing regions. The rapid loss of Arctic cooling snow and ice albedo cooling is projected to increase N. hemisphere drought, so may now be a factor.
LIVESTOCK
The 2007 IPCC assessment found the impact of drought on livestock to be far more than
previous assessments. The impact on animal productivity due to increase variability
in weather patterns will likely be far greater than effects associated with the average
change in climatic conditions. Lack of prior conditioning to weather events most results
in catastrophic losses in confined cattle feedlots (Hahn et al., 2001), with economic
losses from reduced cattle performance exceeding those associated with cattle death
losses by several-fold (Mader, 2003).
A number of studies in Africa (see Table 5.3) and in Mongolia (Batima, 2003) show a strong relationship between drought and animal death. Projected increased temperature, combined with reduced precipitation in some regions (e.g., Southern Africa) would lead to increased loss of domestic herbivores during extreme events in drought-prone areas. With increased heat stress in the future, water requirements for livestock will increase significantly compared with current conditions, so that overgrazing near watering points is likely to expand (Batima et al., 2005).
The 2007 IPCC assessment found the impact of drought on livestock to be far more than
previous assessments. The impact on animal productivity due to increase variability
in weather patterns will likely be far greater than effects associated with the average
change in climatic conditions. Lack of prior conditioning to weather events most results
in catastrophic losses in confined cattle feedlots (Hahn et al., 2001), with economic
losses from reduced cattle performance exceeding those associated with cattle death
losses by several-fold (Mader, 2003).
A number of studies in Africa (see Table 5.3) and in Mongolia (Batima, 2003) show a strong relationship between drought and animal death. Projected increased temperature, combined with reduced precipitation in some regions (e.g., Southern Africa) would lead to increased loss of domestic herbivores during extreme events in drought-prone areas. With increased heat stress in the future, water requirements for livestock will increase significantly compared with current conditions, so that overgrazing near watering points is likely to expand (Batima et al., 2005).

Drought is damaging of course the human population health by lack of water and increase in diseases. In past droughts - millions have died. This will greatly increase the effect of climate change induced food losses to human health and survival shown by the climate crop models .
Climate change through drought and flooding will increase soil erosion/land degradation, already a huge problem being made worse by damaging farming and grazing practices eg China, Africa
Climate change through drought and flooding will increase soil erosion/land degradation, already a huge problem being made worse by damaging farming and grazing practices eg China, Africa

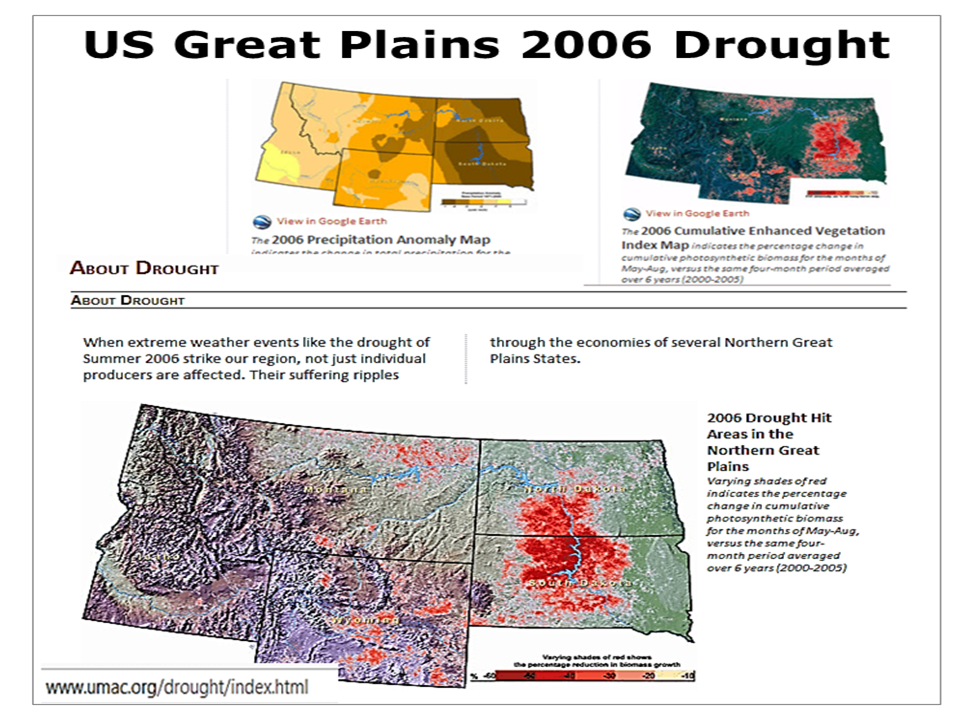
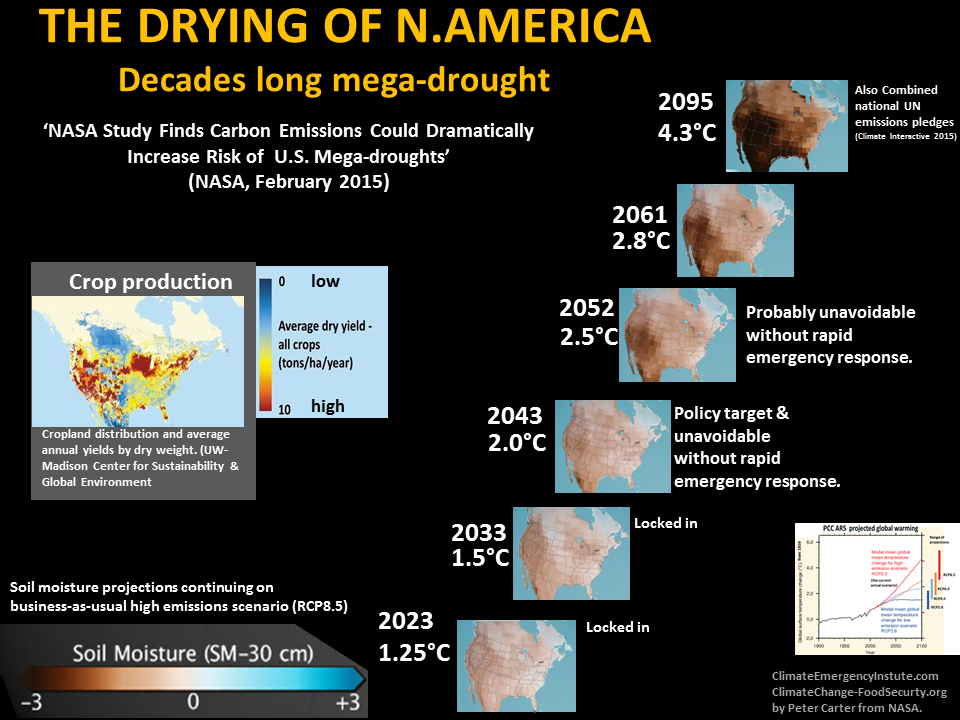
The world's most productive agricultural region is the US Great Plains called the world's breadbasket which stretches up to Canada. This region has a recent history and a far distant history of natural vulnerability to drought, and suffered a major drought in 2006. Climate change is projected to increase plains drought (USGS). The NOAA North American Drought Monitor covers this region. For current US drought check US Drought Portal.
The Future: drought will increase and spread more rapidly
Both (model) projections indicate Southern Europe, North Africa, Mexico, the Caribbean, and a large portion of the United States and Canada will likely to suffer dramatic increases in the incidence of drought.
Floods and Droughts in a Changing Climate – Now and the Future
April 29th, 2011 Paul A. Dirmeyer Center for Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Studies Maryland.
Floods and Droughts in a Changing Climate – Now and the Future
April 29th, 2011 Paul A. Dirmeyer Center for Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Studies Maryland.

The extent of increasing drought extent over the past 50 years according to the PDSI is questioned by new research, though the projection of drought increase with global warming is not in question.
There has been several very severe NH extreme heat - and drought events since 2000.
There has been several very severe NH extreme heat - and drought events since 2000.
There is a long history of episodic severe and long lasting affecting all the world's best food producing regions. Experts at a 2009 WMO workshop agreed that global warming will greatly increase this natural tendency, with increasing heat waves and more drought damage to crops.
The loss of Arctic cooling albedo especially the snow will increase NH heat waves, drought and prolong these extremes.
The loss of Arctic cooling albedo especially the snow will increase NH heat waves, drought and prolong these extremes.


IPCC- drought page
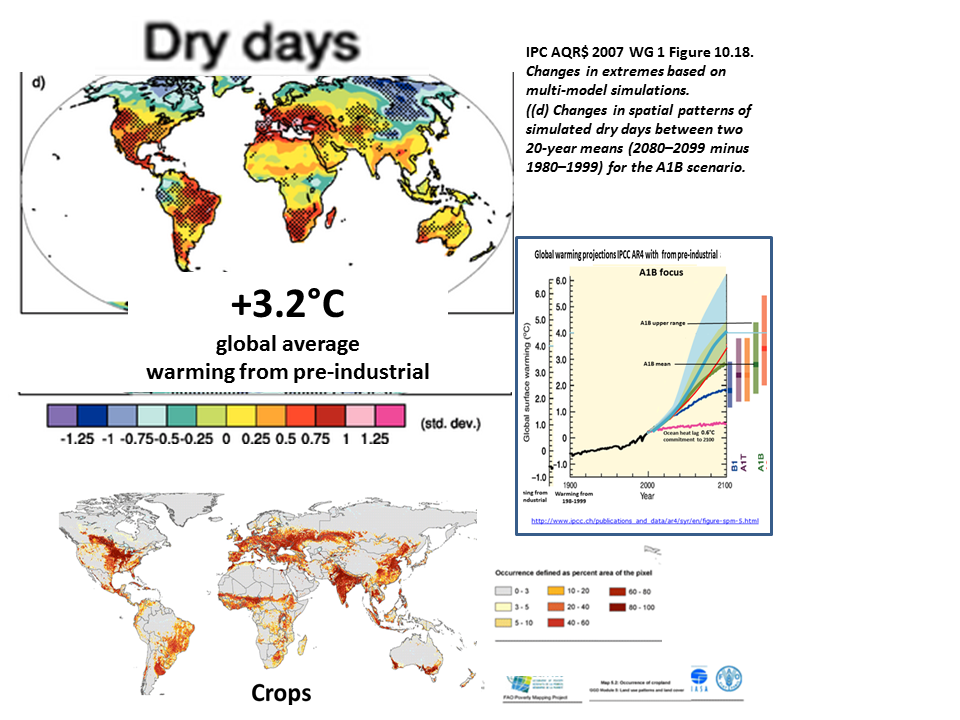
Drought severity will increase. Global warming and changes in drought Aug 2013 K. Trenberth, A Dai,
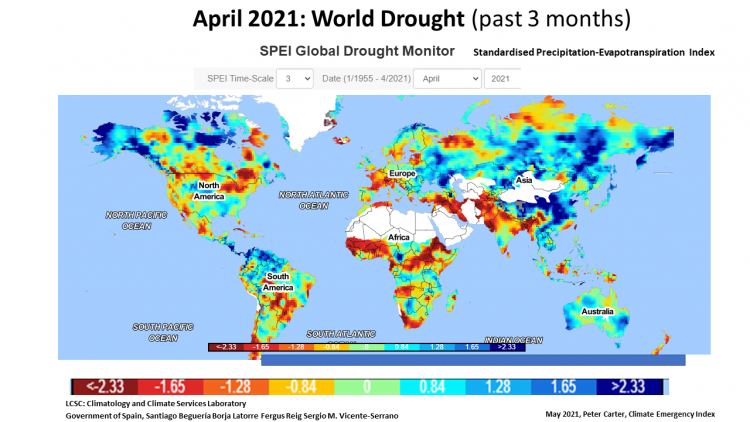
Govt of Spain SPEI Global Drought Monitor
Projections of Future Drought in the Continental United States Lawrence Livermore
IMPACT abrupt change 2009 2011 Paper
Presentation
IMPACT abrupt change 2009 2011 Paper
Presentation
Recent Research
by date
12 May 2021 Evidence of anthropogenic impacts on global drought frequency, duration, and intensity
8 Dec 2020 Increase in Compound Drought and Heatwaves in a Warming World
26 Oct 2020 US corn crop's growing sensitivity to drought revealed
6 Aug 2020 Climate change to bring longer droughts to Europe
by date
12 May 2021 Evidence of anthropogenic impacts on global drought frequency, duration, and intensity
8 Dec 2020 Increase in Compound Drought and Heatwaves in a Warming World
26 Oct 2020 US corn crop's growing sensitivity to drought revealed
6 Aug 2020 Climate change to bring longer droughts to Europe
2 June 2020 Latest climate models show more intense droughts to come
10 May 2020 Twenty-first Century drought projections in the CMIP6 forcing scenarios.
Climate-driven megadrought is emerging in western US, study says
March 2020 Variation trend of global soil moisture and its cause analysis
2 May 2019 Scientists see fingerprint of warming
climate on droughts going back to 1900
2 May 2019 Central American 'Dry corridor' farmers suffer major crop losses- drought & flood
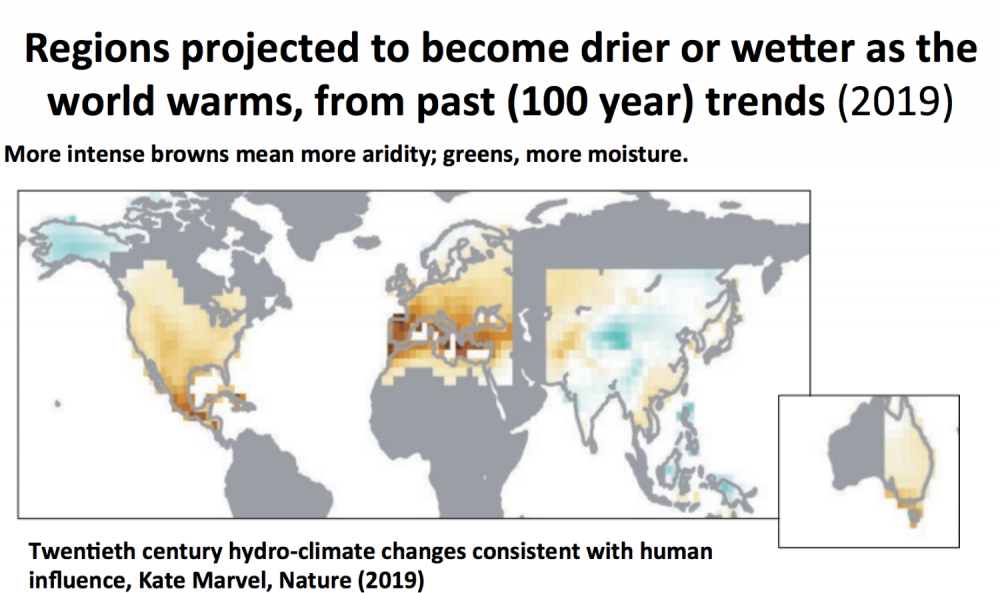
1 May 2019 Twentieth-century hydroclimate changes consistent with human influence
March 2020 Variation trend of global soil moisture and its cause analysis
2 May 2019 Scientists see fingerprint of warming
climate on droughts going back to 1900
2 May 2019 Central American 'Dry corridor' farmers suffer major crop losses- drought & flood
1 May 2019 Twentieth-century hydroclimate changes consistent with human influence
13 Dec 2018 The long dry: Why the world's water supply is shrinking
1 Aug 2018 Climate change-driven droughts are getting hotter
15 March 2018 FAO Climate Change Natural Disasters Are Costing Farming Billions of Dollars a Year Drought the leading cause
Mar 2017 'Traveling' droughts
27 Aug2015 European ‘extreme weather belt’ (2015 drought) linked to worst drought since 2003
March 2015 CO2 increase can intensify future droughts in tropics (& subtropics), Full paper
23 Feb 2015
Robust ...increasing global dryness due to CO2 warming ... model projections
Feb 2015
Unprecedented 21st century drought risk in the American Southwest and Central Plains
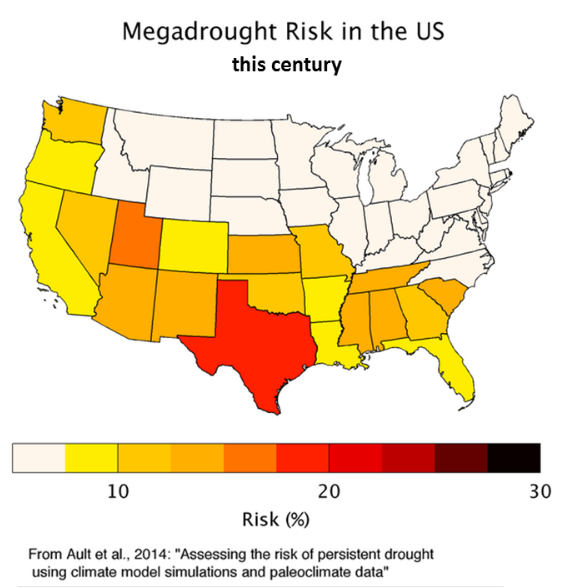
2014 Assessing the Risk of Persistent Drought Using Climate Model Simulations
and Paleoclimate Data
T. R. Ault.
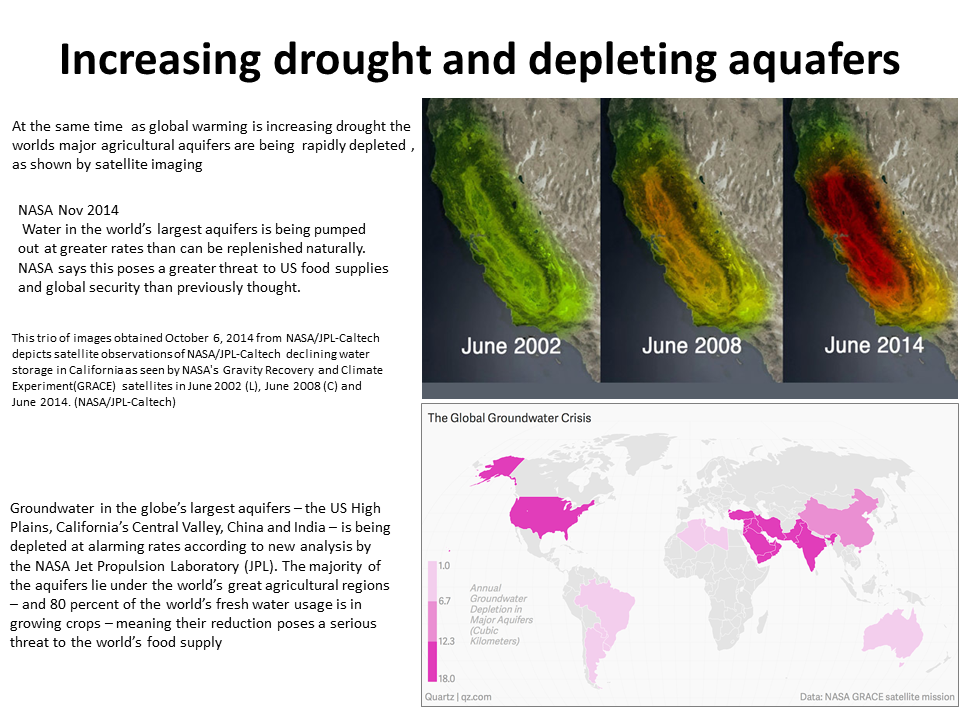
Nov 2014 NASA Major droughts threaten food supply, global security
Sept 2014 California drought linked to climate change
Sept 2014 NA drought The role of temperature in drought projections over North America
August 2014 Assessing the risk of persistent drought - found to be extremely high
June 2014 Responses of terrestrial aridity to global warming
April 2014 GRLS. Wang
California severe drought
linked to global warming.
March 2914 B. Cook Global warming and 21st century drying
Mar 2014 Nature The key role of dry days in changing regional climate and precipitation regimes
July 2012 W. US projects drought crop losses.
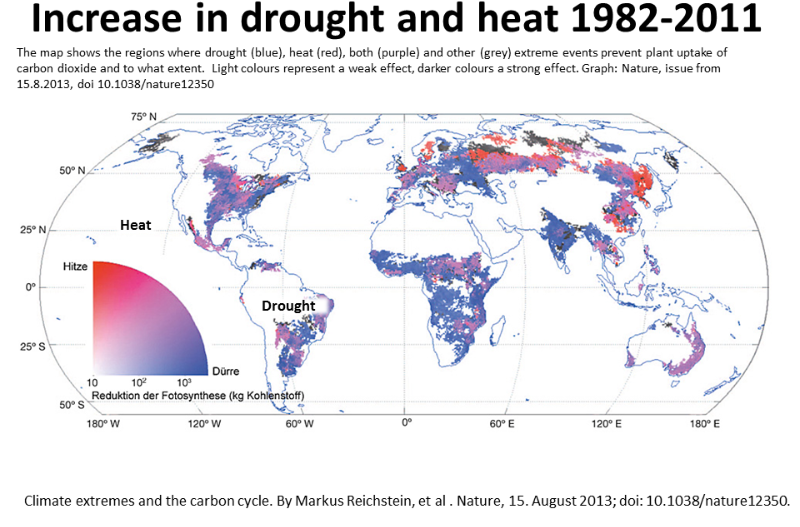
Reduction in carbon uptake during turn of the
century drought in western North America
Christopher R. Schwalm1
1 Aug 2018 Climate change-driven droughts are getting hotter
15 March 2018 FAO Climate Change Natural Disasters Are Costing Farming Billions of Dollars a Year Drought the leading cause
Mar 2017 'Traveling' droughts
27 Aug2015 European ‘extreme weather belt’ (2015 drought) linked to worst drought since 2003
March 2015 CO2 increase can intensify future droughts in tropics (& subtropics), Full paper
23 Feb 2015
Robust ...increasing global dryness due to CO2 warming ... model projections
Feb 2015
Unprecedented 21st century drought risk in the American Southwest and Central Plains
2014 Assessing the Risk of Persistent Drought Using Climate Model Simulations
and Paleoclimate Data
T. R. Ault.
Nov 2014 NASA Major droughts threaten food supply, global security
Sept 2014 California drought linked to climate change
Sept 2014 NA drought The role of temperature in drought projections over North America
August 2014 Assessing the risk of persistent drought - found to be extremely high
June 2014 Responses of terrestrial aridity to global warming
April 2014 GRLS. Wang
California severe drought
linked to global warming.
March 2914 B. Cook Global warming and 21st century drying
Mar 2014 Nature The key role of dry days in changing regional climate and precipitation regimes
July 2012 W. US projects drought crop losses.
Reduction in carbon uptake during turn of the
century drought in western North America
Christopher R. Schwalm1
Sept 2014 Jo Romm coverage on recent drought risk researchGLOBAL WARMING BOOSTS CHANCES
OF CIVILIZATION THREATENING MEGA-DROUGHTS HERE (USA) AND ABROAD.
MARCH 2014 LARGE GLOBAL DROUGHT STUDY:Weather Underground DROUGHTS TO BECOME MORE FREQUENT OVER NEARLY A THIRD OF THE EARTH. EXPECT THE WORLD'S BEST FOOD PRODUCING REGIONS IN THE TEMPERATE NORTHERN HEMISPHERE TO BE HIT BY INCREASING DROUGHT UNDER GLOBAL WARMING AND CLIMATE CHANGE WITH LOSSES TO FOOD SECURITY EVEN WITH ADAPTIVE MEASURES. March 2014 Global warming and 21st. century drying Benjamin I. Cook, Conclusions
OF CIVILIZATION THREATENING MEGA-DROUGHTS HERE (USA) AND ABROAD.
MARCH 2014 LARGE GLOBAL DROUGHT STUDY:Weather Underground DROUGHTS TO BECOME MORE FREQUENT OVER NEARLY A THIRD OF THE EARTH. EXPECT THE WORLD'S BEST FOOD PRODUCING REGIONS IN THE TEMPERATE NORTHERN HEMISPHERE TO BE HIT BY INCREASING DROUGHT UNDER GLOBAL WARMING AND CLIMATE CHANGE WITH LOSSES TO FOOD SECURITY EVEN WITH ADAPTIVE MEASURES. March 2014 Global warming and 21st. century drying Benjamin I. Cook, Conclusions
Oct 2014 EU 'With global warming, the world is likely to become increasingly prone to drought events. About half of the Earth’s land area is susceptible to drought, which killed more than 11 million and affected more than 2 billion people from 1900 to 2011. Over the past decades, droughts have become more recurrent in Europe, causing approximately 100 billion Euros of damage from 1976 to 2006.'

Nov 2014 NASA: Major droughts threaten food supply, global security
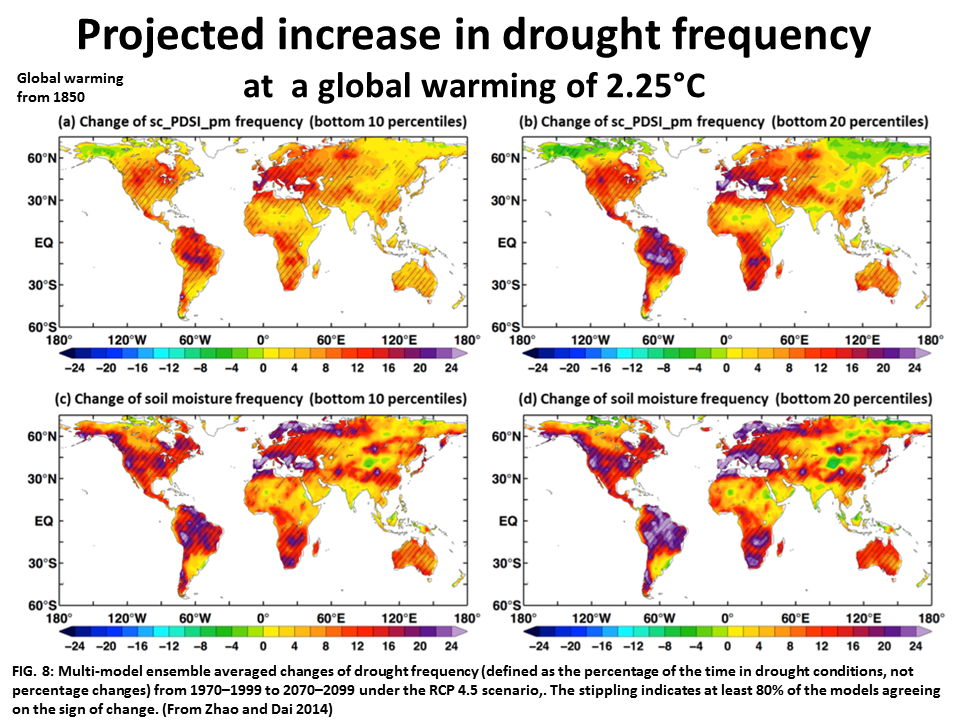

The 2015 N. America drought research confirms the extensive severe drought increase of A Dai's 2010 research that increasing drought could affect much of the world within decades. Under the 2C policy target most of the world will suffer severe drought, with decade long drought for some major food producing regions,and mega-droughts for a few regions.
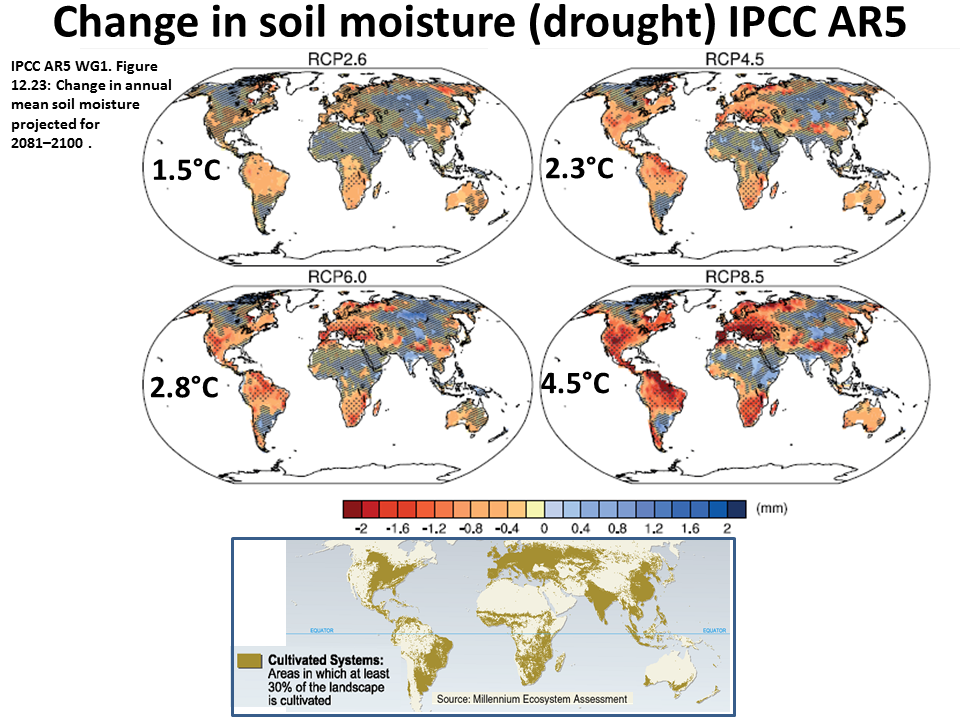
1 Oct 2018Drought losses in China will soar with continuing global warming
Sept 2015 Lake Powell's receding waters
show risk of U.S. "megadrought"
2015 research projects increasing severe drought
in the US and other crucial regions.
March 2015 Increases in atmospheric CO2 could intensify extreme droughts in tropical and subtropical regions—such as Australia, the southwest and central United States, and southern Amazonia—at much a faster rate than previously anticipated.
Feb 2015 Unprecedented 21st century drought risk in the American Southwest and Central Plains.
Sept 2015 Lake Powell's receding waters
show risk of U.S. "megadrought"
2015 research projects increasing severe drought
in the US and other crucial regions.
March 2015 Increases in atmospheric CO2 could intensify extreme droughts in tropical and subtropical regions—such as Australia, the southwest and central United States, and southern Amazonia—at much a faster rate than previously anticipated.
Feb 2015 Unprecedented 21st century drought risk in the American Southwest and Central Plains.

dr


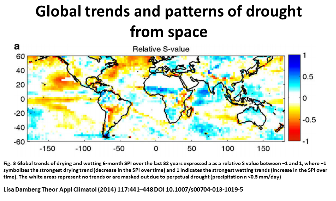
Drought is increasing regionally with climate change from records and now satellite data.
Below is the 2015 Global trend analysis of the MODIS drought severity index (2000-2015)
Note China
The 2014 IPCC AR5 reports increasing regional drought,which will continue.
Below is the 2015 Global trend analysis of the MODIS drought severity index (2000-2015)
Note China
The 2014 IPCC AR5 reports increasing regional drought,which will continue.
Increasing regional drought with
projections of increasing world wide drought
projections of increasing world wide drought
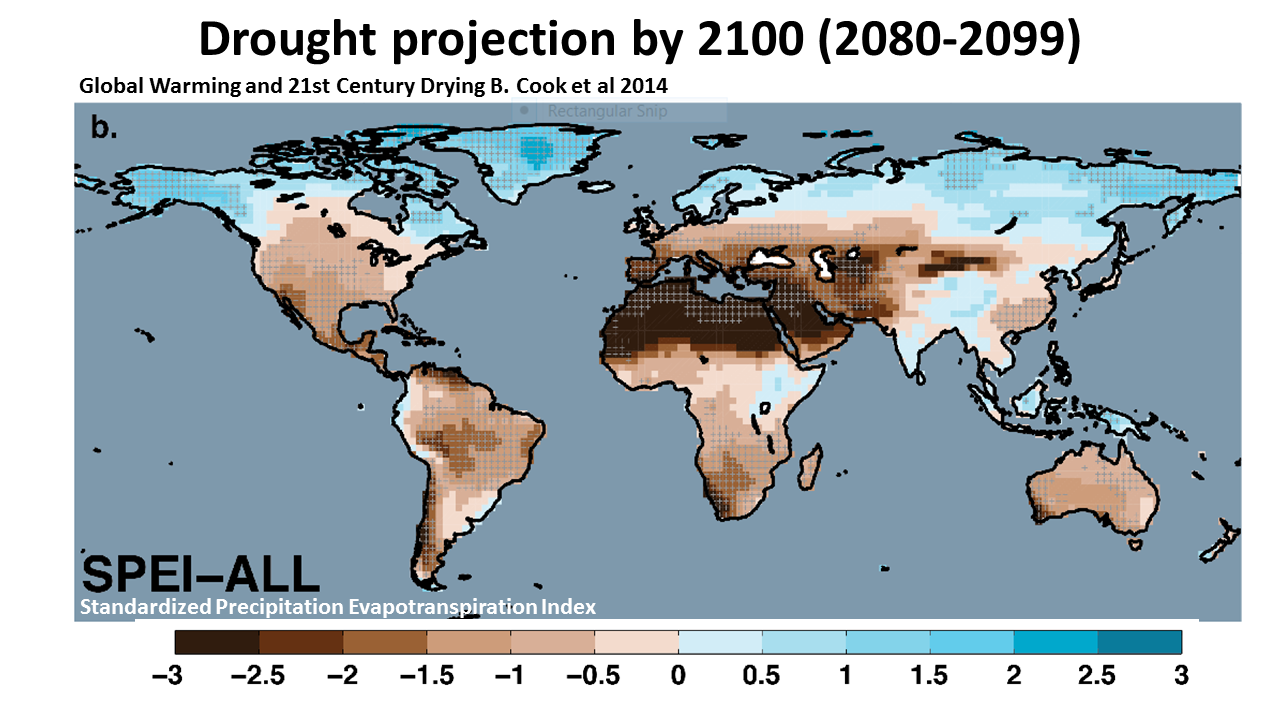
A definitive 2014 NASA study projects 'robust cross-model drying in western North America,
Central America,
the Mediterranean, southern Africa, and the Amazon'.
Drought intensifies and spreads.
Central America,
the Mediterranean, southern Africa, and the Amazon'.
Drought intensifies and spreads.
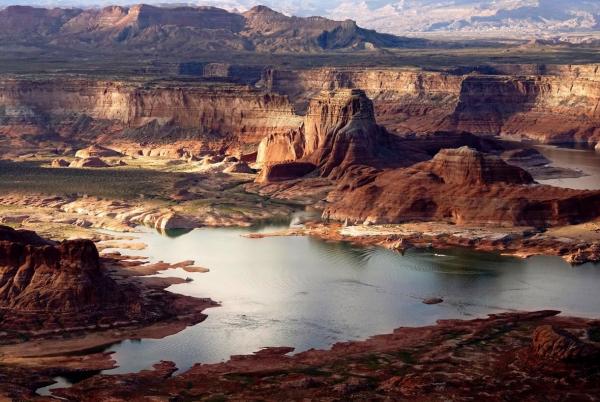

Lake Powell
24 Oct 2017 World Bank Uncharted Waters...21st century collision of two powerful trends—rising populations coupled with a changing climate. With population growth, the demand for water is growing exponentially while climate change is making rainfall more erratic and less predictable. With climate change,... longer and deeper periods of droughts and deluges. Impacts are deep cascading and long lasting.
The watchers on drought
Up to date drought news
Up to date drought news
Best overall Copernicus Global Drought Observatory
April 2018 FAO The impact of disasters and crises on agriculture and food security The rising incidence of
weather extremes will have increasingly negative impacts on agriculture because critical thresholds are
weather extremes will have increasingly negative impacts on agriculture because critical thresholds are
already being exceeded. Drought causes 83% of all damage and loss to agriculture and 86% to livestock
1 May 2019 Human influence on global droughts goes back 100 years, NASA study finds
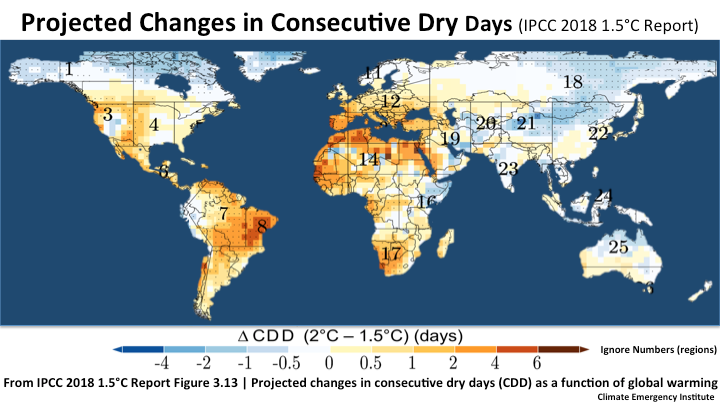
Princeton Climate Analytics Drought
Agroclimate Observatory (FAO, S. America)
16 April 2020Climate-driven megadrought is emerging in western US
June 2020 Latest climate models say more severe droughts to come
12 May 2021 Evidence of anthropogenic impacts on global drought frequency, duration, and intensity