
Climate Change and Food Security
Dual aspect of GHG emissions and food production
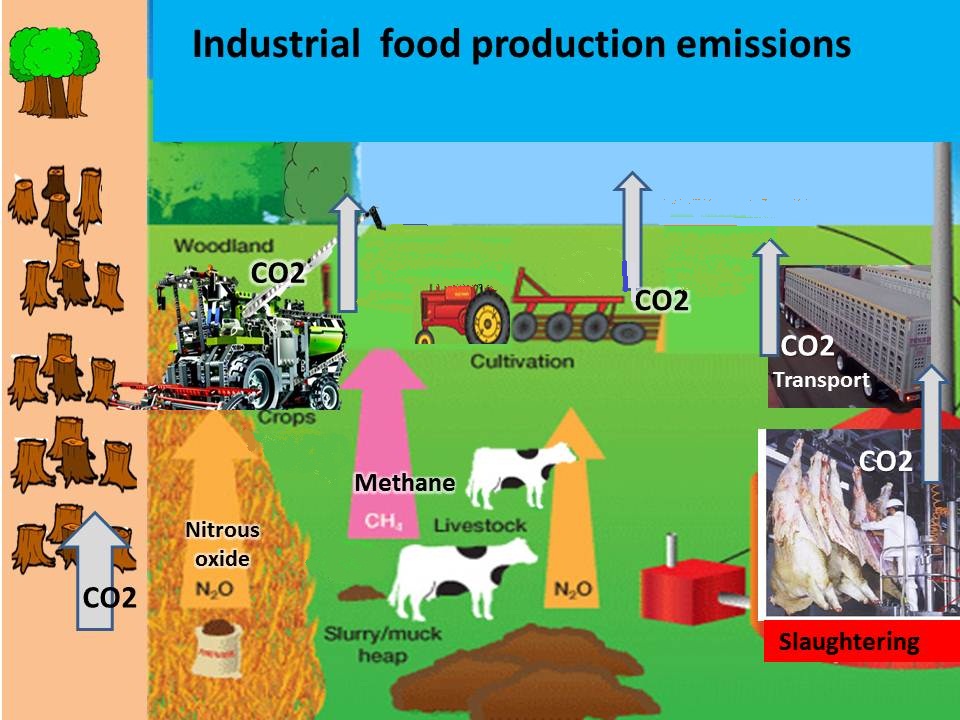

Food production is both a victim of global climate change and a cause,
by being a source of all three main GHGs and a major cause of global warming
Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge
Food production GHG sources
CO2:
deforestation for pasture, food transport
Methane:
livestock
Nitrous oxide:
chemical fertilizer, livestock wastes
The fact that food production is both damaged by GHGs and a source of GHGs makes it doubly important that climate change and food security be given top priority.
This is not the case at present. Both aspects are being practically ignored, all attention being given to fossil fuel CO2 emissions.
If we don't control food production emissions our food production today will damage food production in a few decades from today.
So our food security depends on changing food production practices today to control emissions - as well as stopping fossil fuel CO2 emissions.
So our food security depends on changing food production practices today to control emissions - as well as stopping fossil fuel CO2 emissions.
GHG atmospheric pollution impacts on food
This a very complicated chart, and that is its point.
This a very complicated chart, and that is its point.
There are a great many adverse impacts of GHG pollution caused global warming and climate change on food productivity.
Fossil fuel air pollution damages crops by acid rain and in particular by ground level ozone air pollution. This ozone is formed by heat catalyzing a chemical reaction of fossil fuel air pollutants (VOCs) to form ozone in the ambient air.
Ozone in our air is toxic to our health and it is also toxic to green plants impairing their capacity to grow by photosynthesis.
< Agriculture
GHG emissions >
FEEDING CLIMATE CHANGE
June 2016 OXFAM What the Paris Agreement means for food and beverage
companies. Article on report
June 2016 OXFAM What the Paris Agreement means for food and beverage
companies. Article on report
Food emissions at18 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide eq are 34 per cent, though down from 44 per cent in 1990, UN 2021
1 April 2021 Climate change causes food production losses - cut global farming productivity 21% since 1960s